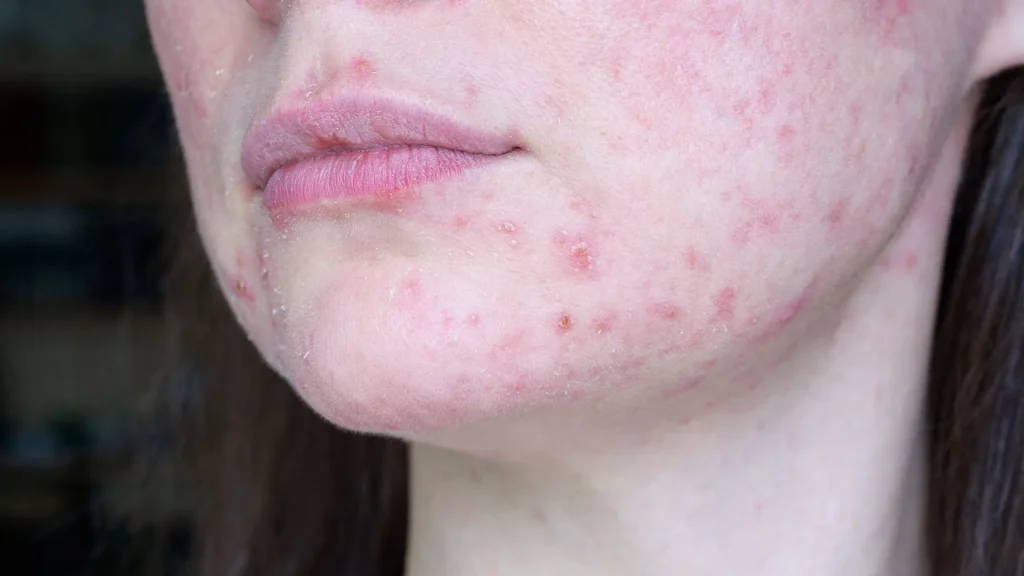
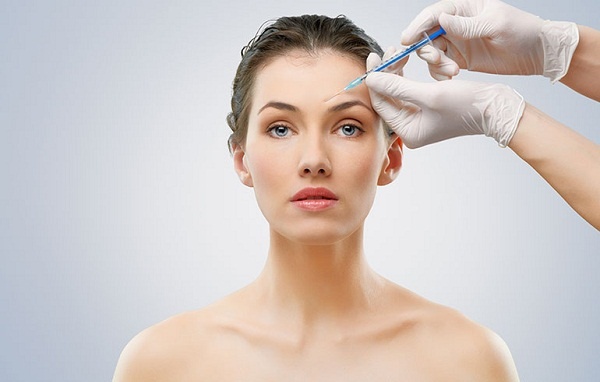
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is one of the most common and persistent sequelae following inflammatory acne. Even after acne lesions have healed, residual dark spots often remain, significantly affecting facial aesthetics and patient confidence. In many cases, these pigmentary changes are more distressing than acne itself.
In Asian populations, including patients in Vietnam, Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation tends to be more pronounced and longer-lasting due to higher baseline melanocyte activity and increased susceptibility to post-inflammatory pigmentation. Environmental factors such as ultraviolet radiation, air pollution, and delayed acne treatment further contribute to this condition.
While topical therapies remain the foundation of PIH management, laser and light-based therapies have become increasingly important, particularly for patients with moderate to severe pigmentation or those who respond poorly to topical agents alone. At a specialized dermatology clinic in Ho Chi Minh City, these technologies allow targeted treatment of pigment while minimizing damage to surrounding tissue.
At Citrine Derma Clinic, a reputable dermatology clinic in District 7, laser and light-based modalities are selected and customized by experienced dermatologists based on individual skin type, pigmentation depth, and clinical severity. This article provides a comprehensive, evidence-based overview of laser, IPL, and LED therapies for post-acne hyperpigmentation, supported by current dermatologic literature [1–3].
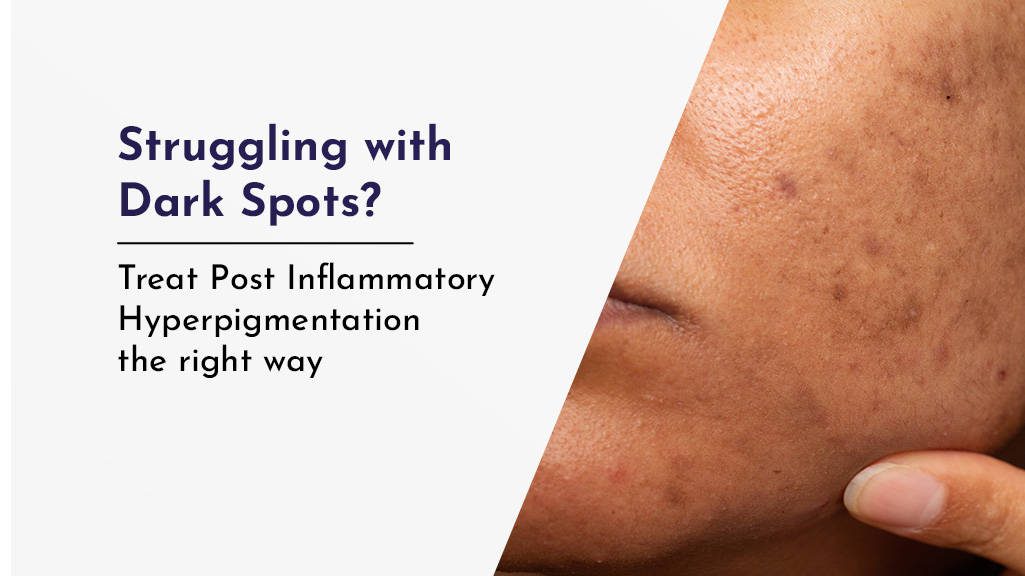
How to treat PIH the right way?
Pathophysiology of Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and Rationale for Energy-Based Treatments
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is a subtype of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation caused by:
- Inflammatory mediators stimulating melanocytes
- Increased melanin synthesis via tyrosinase activation
- Abnormal melanin deposition in the epidermis or dermis
- Exacerbation by ultraviolet exposure
Energy-based devices target melanin or inflammatory pathways through selective photothermolysis or photobiomodulation, making them valuable tools in comprehensive PIH management.
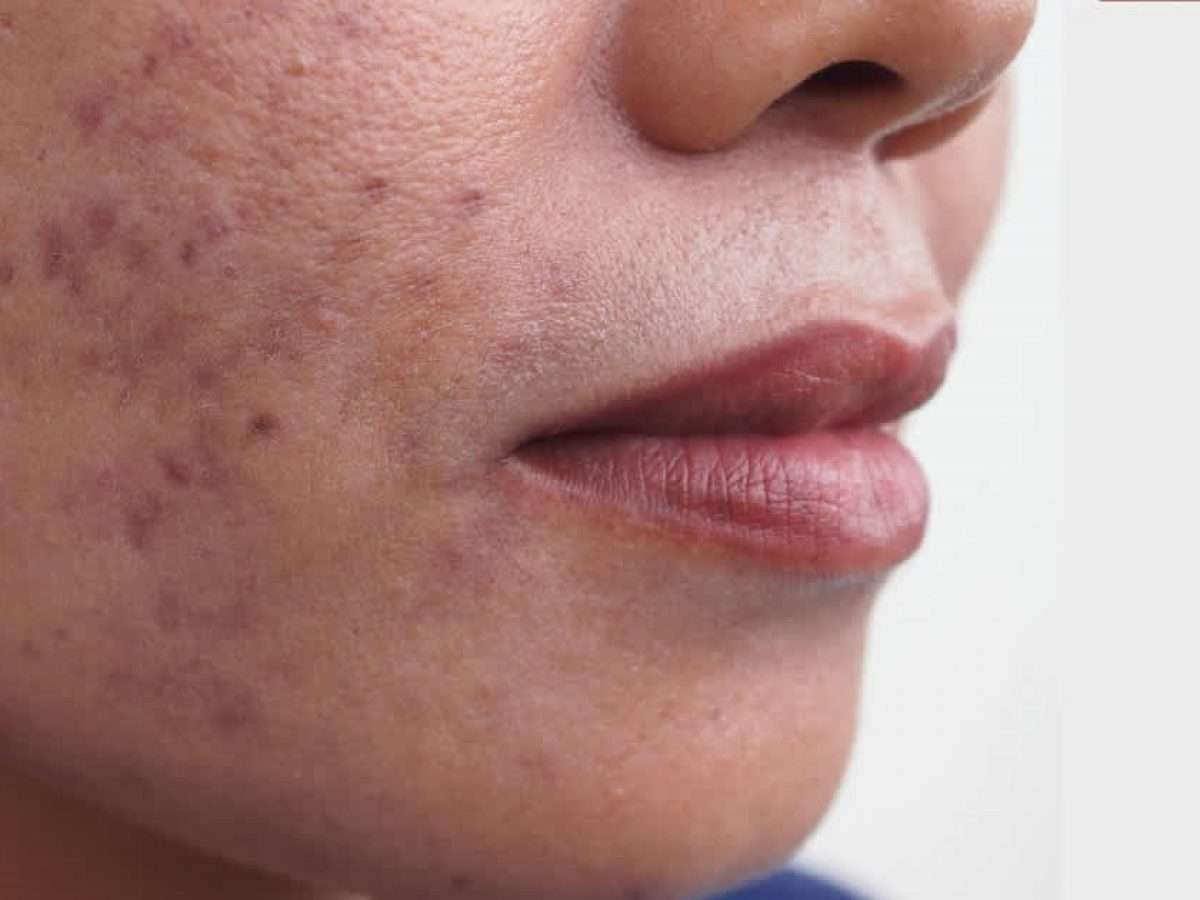
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH)
Overview of laser and light-based modalities
Laser and light-based therapies for PIH can be broadly classified into:
- Pigment-targeting lasers
- Fractional lasers
- Intense pulsed light (IPL)
- Light-emitting diode (LED) therapy
Each modality differs in wavelength, depth of penetration, and clinical application, requiring careful selection by a good dermatologist.
Laser therapies for Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
a. Q-Switched and Picosecond Lasers
Mechanism of Action
These lasers emit high-energy pulses in extremely short durations, selectively targeting melanin granules and fragmenting pigment particles without significant thermal damage to surrounding tissue. The low-fluence Q-switched Nd:YAG and picosecond lasers can effectively reduce PIH, particularly when conservative parameters are used in skin of color [3].
Considerations
- Multiple sessions are often required
- Risk of rebound hyperpigmentation if parameters are too aggressive
- Strict photoprotection is essential
At Citrine Derma Clinic, laser parameters are meticulously adjusted to ensure safety for Asian skin types, reinforcing its reputation as a good dermatology clinic in District 7.
b. Fractional Lasers (Ablative and Non-Ablative)
Mechanism of Action
Fractional lasers create microscopic treatment zones, stimulating dermal remodeling and accelerating pigment clearance through controlled skin regeneration. Fractional lasers are particularly useful for patients with mixed Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and acne scarring [2].
Limitations
- Downtime varies depending on laser type
- Higher risk of PIH if post-treatment care is inadequate
These procedures should only be performed at a specialized dermatology clinic in Ho Chi Minh City with experienced dermatologists.
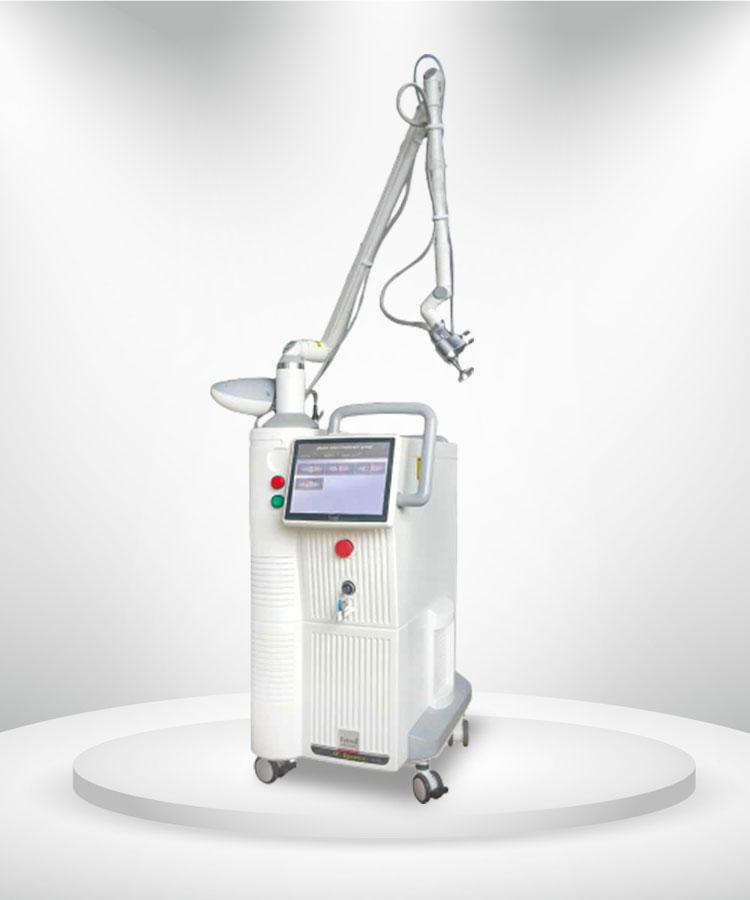
CO2 Fractional Laser
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) therapy
a. Mechanism of Action
IPL delivers broad-spectrum light that targets melanin and hemoglobin, providing:
- Pigment lightening
- Reduction of post-acne erythema
- Anti-inflammatory effects
IPL is effective in correcting the post-acne symptom complex, including hyperpigmentation and residual redness, particularly in mild to moderate cases [1].
b. Advantages
- Non-invasive
- Minimal downtime
- Suitable for early or superficial pigmentation
Lc. imitations
- Less selective than lasers
- Requires cautious use in darker skin types
At Citrine Derma Clinic, IPL is often combined with topical therapy to enhance outcomes, under the supervision of a good dermatologist in District 7.
LED light therapy
Mechanism of Action
LED therapy utilizes specific wavelengths (red, blue, near-infrared) to modulate cellular activity:
- Reduction of inflammation
- Enhancement of skin healing
- Support of post-procedure recovery
LED therapy is primarily an adjunctive treatment, supporting pigment reduction and reducing the risk of post-inflammatory complications following laser or IPL procedures.
Dermatologists at Citrine Derma Clinic frequently incorporate LED therapy into comprehensive treatment plans to optimize patient comfort and recovery.
Factors Influencing Treatment Selection
Successful treatment of Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation depends on:
- Fitzpatrick skin phototype
- Depth and severity of pigmentation
- Ongoing acne activity
- History of previous treatments
A good dermatologist will individualize therapy rather than relying on a one-size-fits-all approach.
Combination therapy: The gold standard
Current evidence strongly supports combination therapy, integrating:
- Laser or IPL treatments
- Topical depigmenting agents
- Strict photoprotection
This multimodal strategy improves efficacy while minimizing adverse effects. As a trusted dermatology clinic in District 7, Citrine Derma Clinic prioritizes combination protocols tailored to each patient.
Safety, adverse effects, and risk management
Potential adverse effects of laser and light-based therapies include:
- Transient erythema
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
- Rare hypopigmentation
Risk is significantly reduced when treatments are performed by experienced professionals and followed by appropriate aftercare.
Why choose Citrine Derma Clinic?
As a leading dermatology clinic in Ho Chi Minh City, Citrine Derma Clinic is recognized for:
- Evidence-based dermatologic treatments
- Advanced laser and light-based technologies
- Personalized care by experienced dermatologists
- Commitment to safety in skin of color
Patients seeking a good dermatologist in District 7 can trust Citrine Derma Clinic for professional and ethical care.
Conclusion
Laser and light-based therapies play an increasingly important role in the management of post-acne hyperpigmentation, particularly in patients with moderate to severe or treatment-resistant pigmentation. When guided by clinical evidence and expert dermatologic judgment, these technologies offer effective and safe solutions.
Supported by current literature [1–3], Citrine Derma Clinic continues to deliver individualized, high-quality care, positioning itself as a premier dermatology clinic in Ho Chi Minh City and a reliable destination for patients seeking long-term improvement in skin tone and clarity.
References
- Kochergin, N. G., & Romanishko, V. V. (2025). Possibilities of intense pulsed light therapy in correcting the post-acne symptom complex. Russian Journal of Skin and Venereal Diseases, 28(2), 212–218.
- Auffret, N., Leccia, M. T., Ballanger, F., Claudel, J. P., Dahan, S., & Dréno, B. (2025). Acne-induced post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation: From grading to treatment. Acta Dermato-Venereologica, 105, 42925.
- Sowash, M., & Alster, T. (2023). Review of laser treatments for post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in skin of color. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology, 24(3), 381–396.
- Điều Trị Da Nhạy Cảm Không Còn Khó – Giải Pháp Kết Hợp Đa Công Nghệ Tại Citrine
- 5 Lý Do Nên Chọn Citrine Derma Clinic Để Điều Trị Nám Và Tàn Nhang
- Top Các Phương Pháp Trẻ Hóa Da Vùng Cổ Được Ưa Chuộng Nhất Hiện Nay
- Bệnh Chàm Da Mạn Tính – Điều Trị Đúng Cách Để Tránh Thâm & Phục Hồi Da Tối Ưu
- Công Nghệ Fotona 6D Honeycomb – Bước Ngoặt Trong Trẻ Hóa Da An Toàn & Lâu Dài